Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of improving a website’s visibility in organic (non-paid) search engine results. The goal is to help search engines understand what the content is about so it can be ranked higher in results for relevant searches.
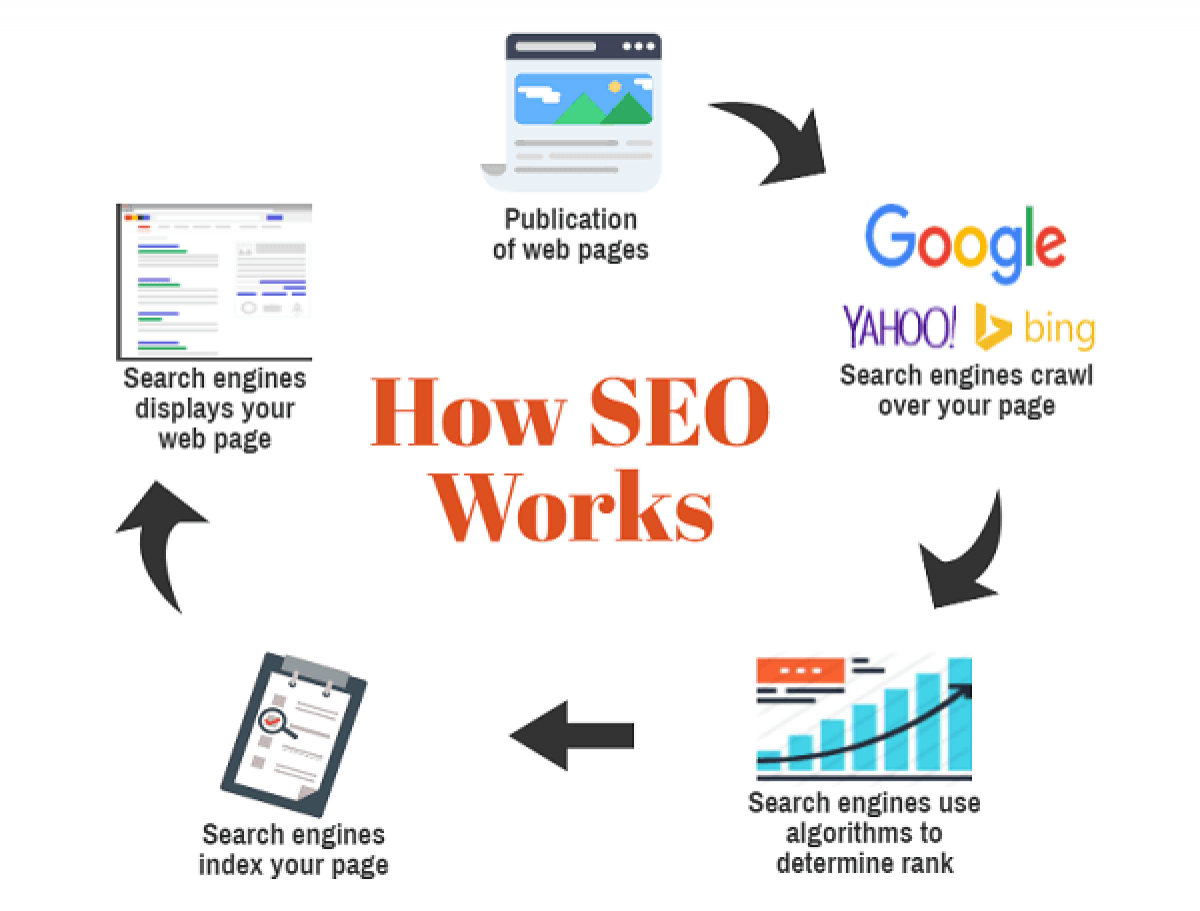
There are many factors that influence search engine rankings, but some key elements of SEO include:
Using Relevant Keywords
Choosing strategic keywords that are relevant to the content helps search engines understand what each page is about. Keywords should be used naturally throughout the content without over-optimizing or “stuffing” too many instances of the same word or phrase. The seed keyword “how SEO works” is used in this article along with related terms.
Creating Descriptive Titles and Headings
Titles and headlines using keywords signal to search engines the topic of the content below. Headings also help indicate sections and structure. Unique, descriptive titles and headings are used throughout this piece.
Writing Informative, Useful Content
The content itself needs to be high-quality, factually accurate, and valuable to readers. Search engines reward pages that satisfy searchers’ needs with comprehensive information and clarity. This article aims to explain clearly how SEO works.
Easy to Navigate Structure
Logically organizing information with sections makes it easier for search engines to crawl and humans to digest. This article uses sections, lists, tables, and other elements to communicate complex ideas about SEO effectively.
Optimizing for Mobile and Speed
With a majority of searches occurring on phones, it’s vital for websites and pages to work seamlessly on mobile. Site speed also impacts rankings, as fast loading pages lead to better user experience. Technical optimizations for mobile-friendliness and site performance enable higher positions.
When used properly, these SEO best practices can help pages rank better organically without resorting to tactics like keyword stuffing that violate search engine guidelines. Below we’ll explore SEO in more depth.
How Search Engines Work
To understand SEO, it helps to know a bit about how search engines operate. The three major functions are:
- Crawling: Search bots navigate (“crawl”) the web and index pages.
- Indexing: Data about pages get stored in an index.
- Ranking: Pages that match search queries best get ranked highest.
There are over 200 ranking factors search engines use, including:
- Page content
- Keyword usage
- Site speed
- Mobile optimization
- Link quality/quantity
- Trust and authority
- Click-through-rates
- Visitor engagement metrics
Optimizing appropriately for the main factors that matter most to search engines can improve rankings organically over time.
Keyword Research
Conducting thorough keyword research is key to an effective SEO strategy. Main goals include:
- Identifying relevant keyword terms and phrases searchers are using.
- Analyzing search volume and competition for keywords.
- Selecting strategic keywords to target.
Seed keywords, like “SEO” here, should be supplemented with long-tail keyword variations as well (such as “beginners guide to SEO”). Going after only high traffic keywords is often an inefficient approach. Expanding into targeted long tail keywords yields easier wins.
Keyword mapping documents all variations paired with topics and pages. Ongoing analysis guides strategic optimization across the site over time.
Table showing example keyword mapping
On-Page Optimization
After selecting target keywords, next steps are on-page optimization to help search bots better understand relevancy to those terms.
Key elements include:
URLs and Titles
- URLs – Contain primary keyword when possible.
- Page Titles – Include keyword early in title tagging.
Headings
- H1, H2 tags – Include keywords in headings to indicate relevancy.
Content
- Keyword density – Use keywords naturally, don’t overstuff. Target is 1-5% generally.
- Image file naming/ALT tags – Use keywords when applicable.
- Links – Anchor text includes keywords for pages linking internally.
Technical
- Mobile friendly – Use responsive design for all devices.
- Site speed – Optimize images, code, etc to improve load times.
- Structured data – Use schema.org standards to enhance rich results.
Proper on-page optimization signals search bots about the main focus of each page tied to keywords. Plus offers better user experience that longer-term leads to higher rankings.
Link Building for SEO
Gaining quality backlinks pointing to your site can significantly boost rankings and authority over time. But link building should provide added value, not just links. Some best practices include:
Earn Links Naturally
Aim for editorially given links, like:
- Mentions in roundup articles
- Interviews on industry websites
- Guest contributions with backlinks
- Press coverage links
Relationship Building
Connect with influencers, partners, industry experts and media to foster meaningful link opportunities. Be patient – this takes ongoing nurturing over months and years.
Promote Great Assets
Develop and promote valuable, link-worthy resources, like:
- Research reports, ebooks, templates
- Tools, calculators, quizzes
- Data-driven studies and industry analysis
Strategic Outreach
Proactively reach out to both small and large websites that might be interested in your content assets or expertise. Personalized pitches tend to work best.
Link building approaches via assets, outreach and relationships
Getting links should add value for others while also benefiting your own site and audience. By establishing yourself as an industry thought leader over time, earned links will keep accruing. Patience and persistence pay off.
SEO Content Tips
Beyond technical optimization and links, content remains king. Google is getting better at understanding language, answering questions, and assessing page quality and E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness). Here are some key content tips:
- Solve searcher needs – Answer common questions and provide helpful information people are seeking. Use search queries for inspiration.
- Length and depth – Long-form, comprehensive content is more likely to satisfy complex information needs.
- Media enhancements – Include relevant charts, graphs, images and videos to engage visitors and reinforce points.
- Actionable advice – Where applicable, include step-by-step advice, guidelines, or instructions to help readers apply solutions.
- Sources and quotes – Cite trustworthy external sources and quotes to validate accuracy and build credibility.
By focusing on optimizing content for creating value, rankings tend to follow. Search engines reward pages that satisfy searchers deepest needs.
Tracking SEO Results
SEO takes patience and commitment before seeing tangible results in rankings and traffic for competitive keywords. How do you track progress?
It’s important to establish key benchmarks, metrics and reporting to monitor results and inform strategy adjustments. Some key performance indicators to measure include:
- Keyword rankings
- Organic traffic
- Conversions
- Links gained
- Engagement metrics
Set realistic goals for traffic and conversions from organic search for your top targeted keyword groups and track at monthly intervals. Adapt SEO efforts based on what’s making the most impact over time.
Conclusion
When used ethically, SEO best practices enable your content to be discovered more often in search engines. By focusing efforts around relevance, quality content and delivering real value for searchers over the long run, organic search visibility and conversions keep growing. Avoid quick fixes and focus on scalable, sustainable solutions.
Knowing how to do effective SEO yourself is a valuable skill for any business.
Hopefully this guide has provided a helpful SEO overview to better optimize your website content by understanding how search engines work and what factors matter most. The key is focusing on great content while leveraging best practices to enhance discovery and visibility.
Now that you know how SEO works fundamentally, the next step is to dive deeper into specific optimization strategies and tactics for your site. Please check out the following additional resources for more details on putting these SEO insights into practical action:
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What is the best way to optimize a page for a target keyword?
The best approach is to focus first on creating high-quality content that answers searchers’ questions and meets their needs related to that keyword. Organically work the keyword into page titles, headers, URL, meta descriptions, image alt text, links, and body content without over-optimizing. Ensure technical optimizations like site speed as well. -
How often should I create new blog content for SEO?
Most experts recommend publishing new blog content consistently, at least 1-2 times per month. This provides fresh content to help search bots re-crawl your site regularly, which can yield updated keyword rankings and discovery. -
Can I rank a webpage without getting backlinks?
It is technically possible to rank some pages without earning backlinks, but building quality links remains one of the most important ranking factors. A balanced approach of link building plus on-page optimization is recommended for competitive keywords. -
How long does it take to see SEO results?
Depending on the competitiveness of keywords targeted, it can take 2-4 months or more before measurable organic traffic and conversions occur. For newer sites establishing credibility and backlinks, 6-12 months is often needed to build momentum. SEO is an ongoing process, not a quick fix. -
What are PAA tags and why do they help with SEO?
PAA stands for People Also Ask, a special type of structured data markup that enables a site to display related questions to their content. Adding PAA can help search bots better understand content relevancy and improve click-through-rates. -
How important are reviews and E-A-T for SEO?
Google is placing increased weight on expertise/authority/trust markers like positive reviews, author bylines, press mentions and citations. Having signals like these can benefit rankings, so proactively building E-A-T evidence is a rising SEO trend. -
Should I use SEO plugins for WordPress?
Yes, SEO plugins like Yoast SEO help optimize technical elements on WordPress sites “out of the box” for better performance. But plugins alone won’t drive results – they complement overall SEO strategies using the best practice insights shared earlier. -
What should I include in meta descriptions?
Compelling meta descriptions under 160 characters with keywords included often lead to higher click-through rates on search listings. Calls to action, page questions answered, and key benefits help make descriptions more engaging. -
How do I check the mobile-friendliness of my site?
Google offers a Mobile Friendly Test tool to check if your site follows mobile-readiness best practices. It provides a scorecard and recommendations to address issues impacting mobile UX. Fast load speeds and no dead links are also important. -
What type of content should I create to earn the most SEO value?
In-depth guides, data-rich reports, numbers-backed studies, and comprehensive FAQ content tend to attract the most organic search interest over time. These demonstrate expertise while answering complex information needs better. -
Is guest posting still an effective link building tactic?
Guest posting can be effective when landing authors get bio backlinks on reputable industry websites. Blanket guest posting to random blogs has diminished impacts. Focus is key – identify where your target buyers’ attention is. -
How important is site speed for SEO rankings?
Site speed significantly influences rankings in Google’s mobile-first index. Pages taking 3+ seconds to fully load reduce engagement metrics. Optimizing pages (images, code, caching, etc) to load in under 2-3 seconds should be an urgent priority. -
Should I use H1 or H2 for my main page keyword?
Both H1 and H2 headings can be optimized to include selected keywords naturally. Typically H1 headers capture the main page focus, while H2 elements help subdivide content into logical sections associates to keywords. -
Is local SEO different than standard SEO?
Yes, local SEO focuses more on signals like brick-and-mortar address, local business schema markup, Google My Business listing consistency, and reviews unique to a specific geographic area. So optimizations should match the local intent. -
What tools are best for SEO audits and tracking organic traffic?
Some top SEO tools include Ahrefs, SEMRush, Moz Pro, Serpstat, and Google Analytics. Most offer site audits along with rank tracking and organic traffic data tied to keywords targeted. SEO technology keeps advancing rapidly. -
Which is better – SEO or Google Ads?
SEO and Google Ads can work very well together in harmony. SEO drives recurring organic traffic directly, while paid ads offer precise control for optimizing specific campaigns. Integrating both strategies is recommended – start with SEO then amplify with targeted ads.